 Cancer occurs as a result of mutations or abnormal changes in the genes responsible for the regulation of cell growth and cell maintenance changed healthy. That gains the ability to divide without control or order, producing more cells, like him and form a tumor. But over time, changes can “turn on” genes and “turn off” genes in other cell. The found in the nucleus of each cell, which acts as the room “control” of each cancer is an uncontrolled growth cell. Normally, our cells renew themselves through an orderly process of cell growth; healthy cells as new position as the old. To better understand breast cancer, it helps to understand how cancer can develop.
Cancer occurs as a result of mutations or abnormal changes in the genes responsible for the regulation of cell growth and cell maintenance changed healthy. That gains the ability to divide without control or order, producing more cells, like him and form a tumor. But over time, changes can “turn on” genes and “turn off” genes in other cell. The found in the nucleus of each cell, which acts as the room “control” of each cancer is an uncontrolled growth cell. Normally, our cells renew themselves through an orderly process of cell growth; healthy cells as new position as the old. To better understand breast cancer, it helps to understand how cancer can develop.
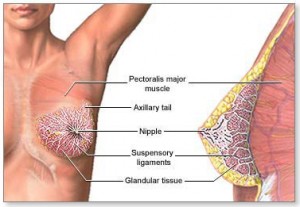
Only 50-10% of cancers arise because of an anomaly inherited from your mother or your father. In general, breast cancer cells, both of lobules, which are milk-producing glands, or ducts, passages to drain the milk lobules nipple. About 90% of breast cancers occur because of genetic abnormalities and due to aging and general “wear”. The term “breast cancer” generally refers to a malignant tumor, which developed into cells in parallel. Less frequently, breast cancer can begin to stoma tissues that contain fat and fibrous connective tissue of the breast.
Breast cancer is never anyone’s fault and has little to do with lifestyle. Learn what you can do to manage the risk of breast cancer factors. Feeling guilty, or telling you that breast cancer has occurred because of something or someone else did, is not productive. There are steps everyone can help the body stay healthy as possible, and a lower risk of developing breast cancer or recurrence of breast cancer (for example, maintain a healthy weight, not smoking, limiting alcohol, and exercising regularly).
While there are general categories, it’s important to speak with your health care team to determine your special circumstances.
- Ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is diagnosed the earliest possible clinical breast cancer and is often diagnosed at screening mammography that has detected small areas of calcification in the breast.
- Infiltrating ductal carcinoma is invasive breast cancer most common, representing 70 percent of all cases.
- Infiltrate tracheal carcinoma accounts for about 5 percent of all malignant, invasive cancer.
- LCIS is thought to be the indicator of an increased risk of developing invasive breast cancer, but not necessarily a direct precursor of invasive breast cancer.
- Only a very small percentage of people who are diagnosed with breast cancer have a few type. Having a rare type that does not mean that survival is worse.
- As a man who was diagnosed with breast cancer, you may have specific problems that do not affect most women.
Instead of only one or two options, there is now an overwhelming menu of treatment options that are fighting the complex mixture of cells in each decision cancer. The – surgery, radiotherapy may be so, hormonal (anti-estrogen) therapy, and / or chemotherapy – can be overwhelming. the treatment advances against breast cancer, bringing new hope and excitement.
The following are the various steps for treatments available for Breast Cancer:
- What types of treatments available, the most likely sequence of treatments, treatment options by cancer stage and treatment facility on your schedule.
- Reasons to get a second opinion on the treatment plan for how to get one, and what to do when you get.
- How is chemotherapy, they should, the different types and combinations, side effects and how to handle.
- How radiotherapy works as it is, the side effects of benefits, and what to expect when you get.
- The link between hormones and breast cancer and how different groups of drugs – including ERD, SERMs and aromatize inhibitors – can affect this relationship.